Where engines, enterprise, and epicurean pursuits meet
Leplanneur brings together three worlds of expertise in one dynamic publication. Explore in-depth guides on automotive technology, business strategy, and culinary techniques that fuel your curiosity and passion.
Explore Our Universes
From the garage to the boardroom to the kitchen
automotive
Cars, vehicles and driving
View articles →business
Business and economy
View articles →cooking
Recipes and culinary arts
View articles →finance & real estate
Finance, investment and property
View articles →health
Health, wellness and wellbeing
View articles →home & living
Home, decor and lifestyle
View articles →News
Latest news and current events
View articles →pets
Pets, animals and companions
View articles →sports
Sports, fitness and competition
View articles →technology
Tech, gadgets and innovation
View articles →woman / fashion
Fashion, beauty and lifestyle
View articles →What Our Readers Say
Trusted by professionals and enthusiasts worldwide
The automotive coverage is incredibly detailed without being overwhelming. I've learned more about engine diagnostics from these articles than anywhere else. The writing makes complex topics accessible.
As a small business owner, I rely on Leplanneur for practical insights I can actually implement. The articles cut through the noise and deliver real value every time.
The cooking guides have transformed my approach to the kitchen. Clear instructions, beautiful photography, and techniques that actually work. This has become my go-to resource.
Latest articles
Our recent publications

Revolutionizing Pet Care: Top Tips Shaping the Future of Animal Health Industry
In recent years, pet care technology has evolved remarkably, offering innovative solutions that enhance pet owners' abil...

Dive into bathroom elegance: a comprehensive guide to choosing the perfect water-resistant wallpaper
Water-resistant wallpaper is a revolutionary solution, particularly beneficial for bathroom design. Its defining trait i...
Boosting Teen Brain Health: The Power of Omega-3 Rich Foods for Mental Wellness
Omega-3 fatty acids are essential for maintaining brain health and promoting overall mental wellness during teenage year...

Essential tips for safely childproofing your home: a comprehensive guide
Childproofing is a crucial aspect of ensuring home safety when little ones are around. It serves as a protective measure...

Enhance Your Wellness Path: The Transformative Power of Outdoor Boot Camps on Physical Fitness
Outdoor boot camps offer a dynamic approach to enhancing physical fitness and mental wellness. They encompass a blend of...

Designing a Peaceful Digital-Free Family Haven: A Modern Homeowner's Guide to Tranquility
Creating a digital-free family haven can remarkably improve household dynamics. One effective approach is setting precis...
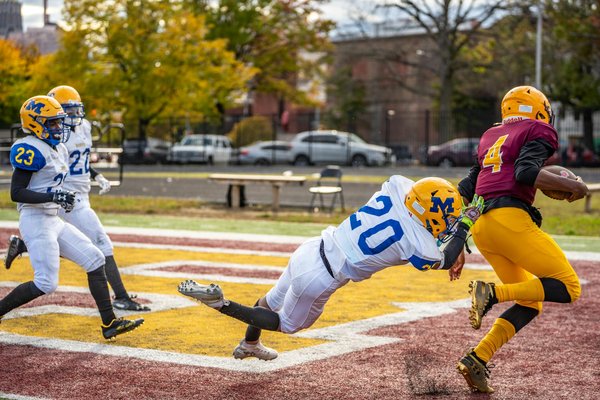

Bespoke Fueling: Personalized Dietary Plans for Endurance Athletes via Precision Nutrition
Precision Nutrition is about designing dietary strategies tailored to individual needs, particularly for athletes in end...
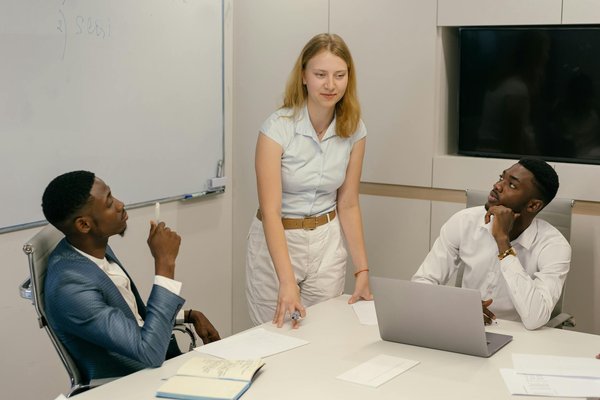

Maximizing Profits: How Tax Incentives Boost Real Estate Investments in Sustainable Development
Tax incentives in real estate serve as crucial financial tools designed to stimulate investments and support sustainable...
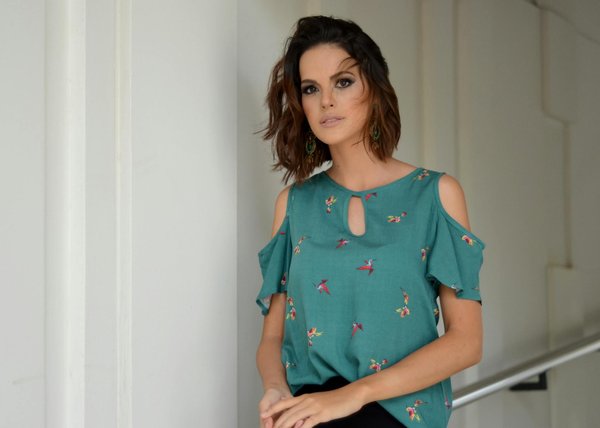

Uncovering How Cultural Districts Shape Urban Real Estate Markets: An Economic Perspective
Cultural districts serve as designated areas within urban settings that are intentionally fostered to nurture the arts a...
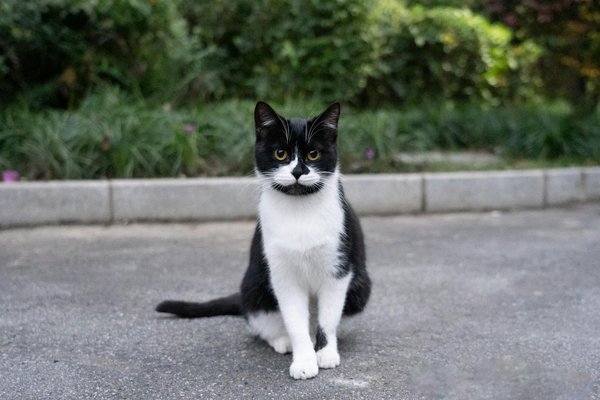

Navigating Legal Hurdles: Transforming Birmingham's Industrial Zones into Residential Havens
Embarking on the journey of transforming industrial zones into residential areas involves navigating several legal chall...

Incorporating seasonal veggies: transform your classic ratatouille recipe
Choosing seasonal vegetables not only enhances the flavour of your dishes but also ensures that you are using the freshe...

Enhance UK School Environments: Proven Methods to Elevate Indoor Air Quality for Better Health and Learning
Understanding indoor air quality and its effects is crucial for school environments. Poor indoor air quality can signifi...

Crafting the perfect coleslaw: a guide to tasty and balanced meal companions
Coleslaw, a versatile dish rich with history, has long been a staple in various culinary traditions. Commonly made from ...

Key Elements to Master for a Successful Subscription Box Startup in the UK
The UK subscription box market has witnessed substantial growth, driven by convenience and personalization. With countle...

Enhance your bmw 5 series sound with easy audio upgrades: a quick guide to minimal tweaks
Enhancing the audio system in your BMW 5 Series can significantly improve your driving experience. Audio upgrades are cr...

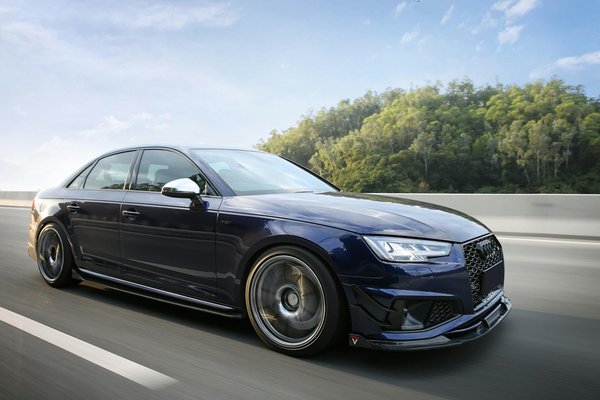
Master the Art of Calibrating Your Audi R8 Digital Dashboard: Proven Strategies for Perfection
The Audi R8 digital dashboard stands out as a marvel of modern automotive engineering, offering drivers a rich tapestry ...

Top strategies for maximizing the durability of your bmw m5 performance clutch
At the heart of any high-performance vehicle, including the BMW M5, lies the performance clutch. Its core function is to...

Innovative Approaches to Using Biodegradable Materials in UK Car Manufacturing
In recent years, biodegradable materials have gained traction in automotive manufacturing due to their potential for pro...

Top mouthwatering marinades for perfectly grilled chicken thighs on the bbq
Marinades are essential for transforming plain chicken thighs into flavorful delights. The right marinade brings depth a...
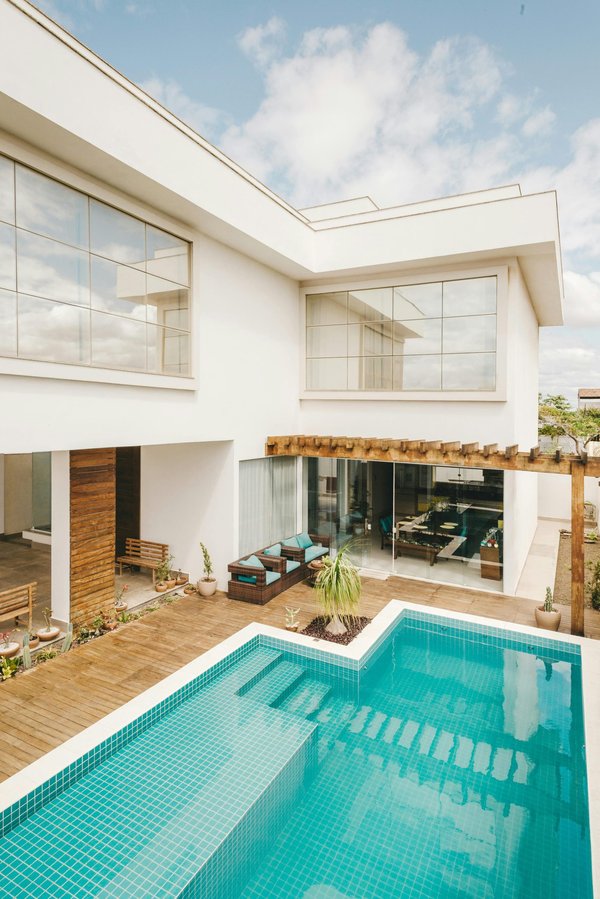

Escape to paradise: ultimate villa rentals in st barth
Discover St Barth's finest villa rentals, where luxury meets stunning views and personalized service. From intimate beac...

How is the UK responding to global trade challenges?
The UK faces significant global trade challenges shaped by a changing international landscape and the lasting effects of...

What Are the Challenges Facing UK News Today?
The UK news industry is grappling with significant financial challenges that are reshaping journalism economics and thre...

What Are the Implications of Recent Policy Changes in UK News?
Recent UK news policy changes have introduced several significant shifts across various sectors, reflecting the governme...

Designing an Ideal Exercise Regimen for Your Pomeranian with Luxating Patella: Tips and Tricks
Luxating patella, a common condition affecting canine joint health, refers to a displaced kneecap. It often occurs due t...

Effective Methods to Calm Your Dog's Fireworks Anxiety: The Ultimate Guide
Fireworks anxiety in dogs is a prevalent issue, characterised by a set of behaviours linked to noise phobia. Dogs manife...

Enhance Your Combat Sports Skills: Unleashing Faster Reflexes with Advanced Neurocognitive Training Techniques
Neurocognitive training is a cutting-edge approach in combat sports, focusing on enhancing reflexes and boosting cogniti...

Enhancing Hurdle Technique: The Power of Real-Time Biomechanical Feedback for Track Athletes
Biomechanical feedback plays a crucial role in enhancing hurdle performance, offering athletes precise insights into the...

The ultimate selection of gel blaster pistols for playtime
Discover the best gel blaster pistols designed for safe, thrilling play. These innovative toys use water-based gel balls...

Top-rated gel blaster pistols for an exciting playtime experience
Top-rated gel blaster pistols offer thrilling playtime with precision and quick action. Selecting the best model hinges ...

Revolutionizing Healthcare: AI Breakthroughs in Medical Imaging Transform Disease Diagnosis
The transformation of healthcare with AI in medical imaging is nothing short of revolutionary. Historically, medical ima...


